
High blood pressure (hypertension) is when the force of blood pumping through the arteries is consistently too high, resulting in the walls of the arteries being expanded beyond their normal limit.
High blood pressure can cause damage and scarring of the artery walls and put people at risk for heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
Blood pressure (BP) is expressed in two numbers:
| Systolic blood pressure (the first/top number) | measures the pressure in the blood vessels when the heart beats |
| Diastolic blood pressure (the second/bottom number) | measures the pressure in the blood vessels when the heart is at rest between beats |
High, elevated, and normal blood pressure is generally defined in the following ranges:
| High blood pressure (hypertension) | 140/90 mmHg or more |
| Elevated blood pressure (prehypertension/at risk for high blood pressure) | between 120/80 and 139/89 mmHg |
| Normal blood pressure | less than 120/80 mmHg |
If you have a BP of 140/90, that is considered high blood pressure and you should discuss this with your doctor. The first thing that is usually recommended for people with high blood pressure to do is lifestyle changes such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Consuming a healthy balanced diet low in salt
- Exercising regularly
- Not smoking
- Limiting or avoiding alcohol
- Managing stress
- Getting adequate sleep
- Taking medications as directed
Medications used to treat high blood pressure include:
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin II antagonists (ARBs)
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Diuretics (“water pills”)
- Peripherally acting alpha-adrenergic blockers
- Centrally-acting alpha adrenergics
- Vasodilators
- Renin inhibitors
- Combination medicines, made up of two or more different kinds of blood pressure medicines
What Are Symptoms of High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure is often called “the silent killer” because it’s common for people to have no warning signs or symptoms.
Uncommonly, severe high blood pressure may cause or be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Vomiting
- Facial flushing
- Blood spots in the eyes (subconjunctival hemorrhage)
- More common in people who also have diabetes
What Causes High Blood Pressure?
Risk factors for developing high blood pressure (hypertension) include:
- Family history of high blood pressure
- Gender
- Race
- African-Americans tend to develop hypertension more often than other races
- Age
How Is High Blood Pressure Diagnosed?
Adults 20 years of age and older should have their blood pressure checked during regular doctor visits.
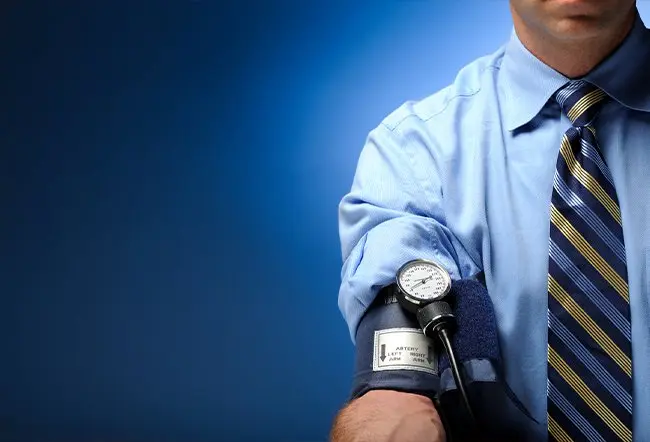
- Blood pressure is measured with a pressure cuff (sphygmomanometer) placed around the upper arm and manually or electronically inflated.
- When inflated, the cuff compresses the brachial artery, the major blood vessel of the upper arm, briefly stopping blood flow.
- The air in the cuff is then released slowly while the person performing the measurement listens with a stethoscope or monitors an electronic readout.
From 
Heart Health Resources
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure
https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/
https://www.fda.gov/consumers/free-publications-women/high-blood-pressure-medicines-help-you